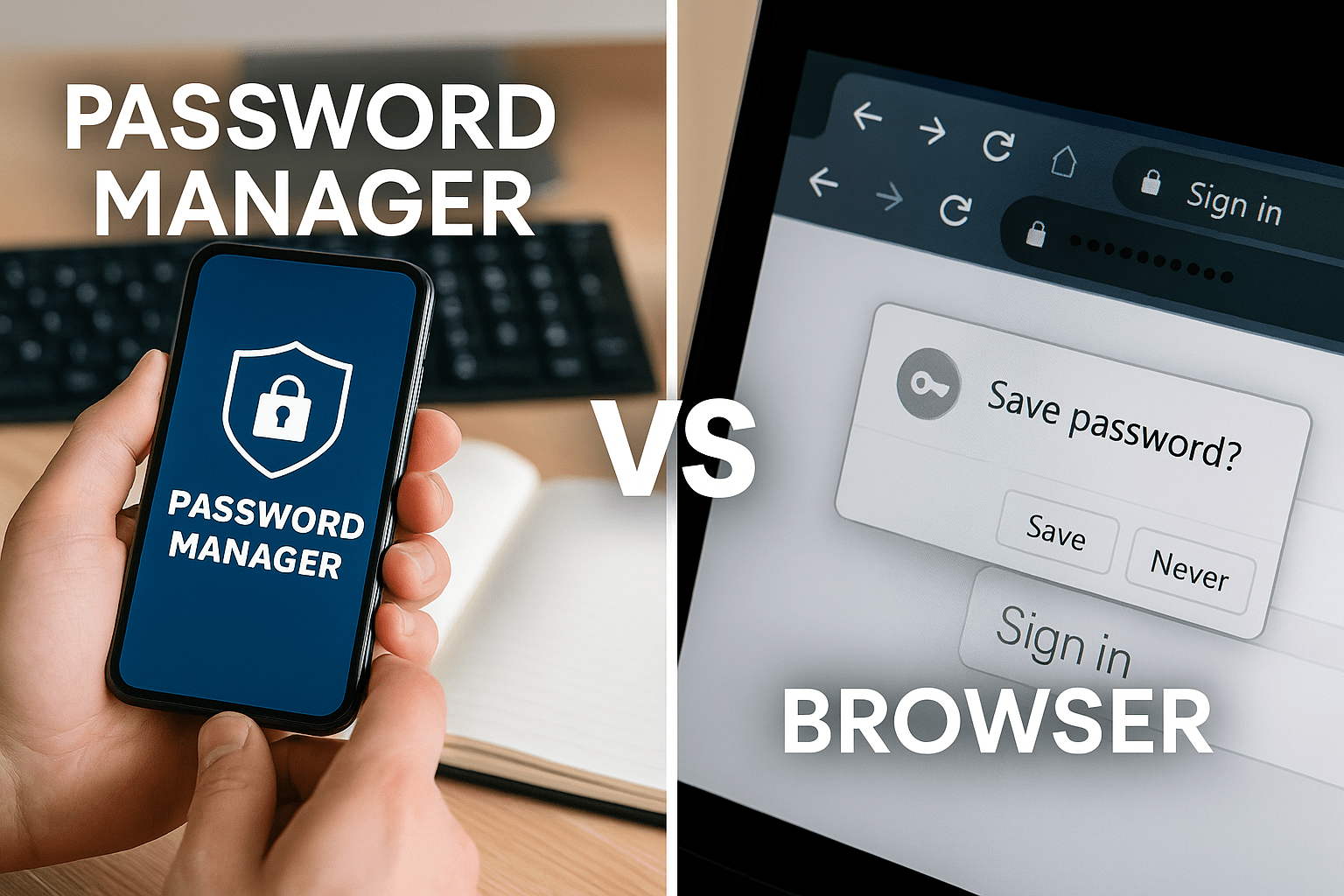
In a world where online accounts and digital access are part of daily life, managing your passwords securely is critical. While both web browsers and dedicated password managers offer to store and autofill your login credentials, they differ significantly in terms of privacy, features, and overall security.
Security and Encryption
Dedicated password managers are built specifically for security. They typically use strong encryption standards like AES-256 to store your data and employ zero-knowledge architecture—meaning not even the service provider can view your information. Most of these tools require a master password and support multi-factor authentication for added protection.
In contrast, browsers often save passwords in less secure environments. While modern browsers encrypt stored credentials, they are still tied to your browser session and may be more vulnerable if your device or profile is compromised.
Cross-Platform Access and Flexibility
Password managers are platform-agnostic. They allow you to access your passwords from different browsers, devices, and operating systems—whether it’s your phone, tablet, or desktop. This ensures consistent, secure access no matter where you are.
Browser-based password storage, on the other hand, is usually restricted to one browser ecosystem. If you’re logged into Chrome, Firefox, or Edge, you may not be able to access your credentials from another browser without manually syncing or exporting.
Advanced Security Features
A dedicated password manager offers more than just storage. Key features often include:
-
Security audits and password strength analysis
-
Data breach alerts for compromised credentials
-
Secure password sharing with trusted users
-
One-time password (OTP) generation
-
Encrypted notes for sensitive data
Browsers offer limited versions of these features—typically just password saving and autofill. They often lack proactive tools for identifying weak or reused passwords.
Phishing Protection
Phishing is one of the most common cybersecurity threats, and password managers are equipped to combat it. They recognize the exact URLs of websites and won’t autofill credentials if a page looks suspicious or doesn’t match the saved domain.
Browsers tend to autofill passwords more liberally. If a phishing site closely mimics the layout of a legitimate site, there’s a higher chance that your credentials could be unknowingly submitted.
Data Portability and Backup
Password managers typically offer options to back up or export your credentials securely, making it easier to migrate or safeguard your information.
Browsers may provide export options, but they are often less user-friendly or require additional tools. Transferring passwords between browsers or devices can be inconsistent and may leave gaps in your password database.
User Control and Privacy
With password managers, you have complete control over your data. You can categorize, tag, and organize credentials however you prefer. You can also store secure notes, credit card details, and even digital IDs in some platforms.
Browsers store passwords primarily for convenience. They don’t usually offer the organizational or privacy customization options that full-fledged managers provide.
Conclusion
Browser-based password storage is convenient for everyday users, especially those who use the same browser across all devices. However, when it comes to serious password management—especially for professionals, businesses, or security-conscious individuals—dedicated password managers offer a much stronger, feature-rich solution.
If your online security matters, investing in a dedicated password manager is a wise step toward safeguarding your digital identity.




Leave A Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.